Introduction
Generally, when talking about VLAN hopping there are two type of attacks, one is called Double Tagging attack which we will be talking about here and the other is spoofing attack. Double Tagging attacks take advantage of a native VLAN trunking configuration in which frames are allowed to be transmitted through VLANs via the trunking port. The attack manipulates the 802.1Q header by adding an extra header which will get stripped off when leaving the switch and forwarded to the trunk port that’s on native VLAN 1. Subsequently, the other switch will forward the packet to the corresponding host on that VLAN. It’s worth noting that the destination of the packet will be based off of the second tag, since the switch only looks at the first VLAN tag it sees.
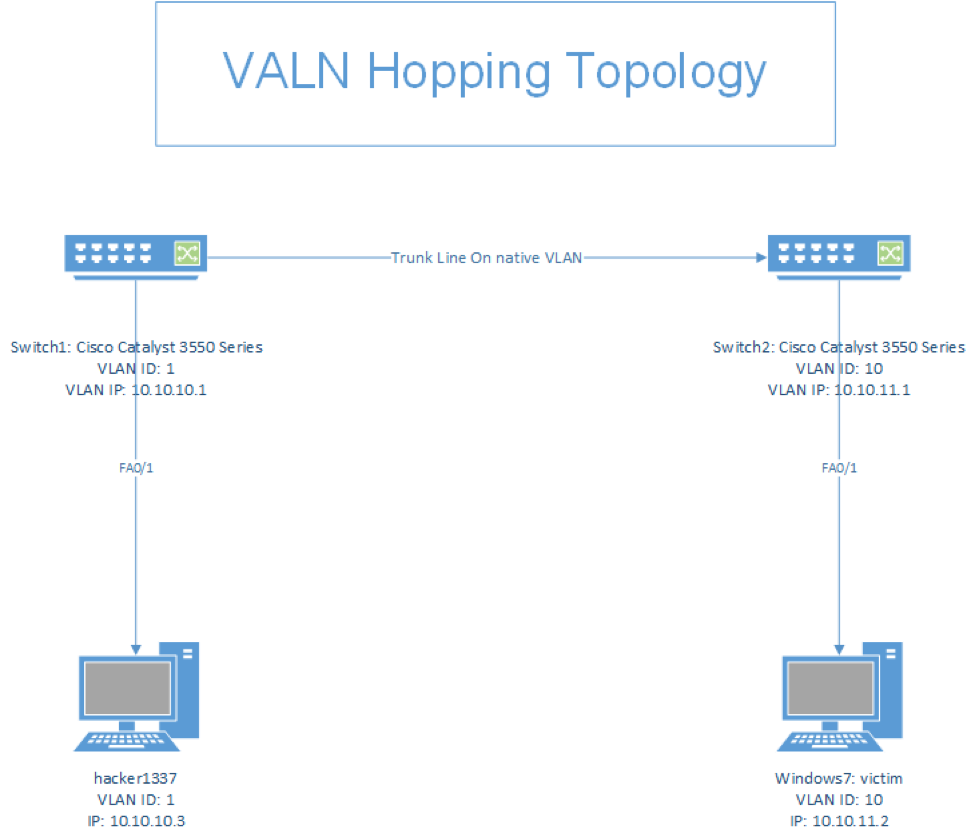
ConstructedTopology
Attack Steps
As shown in my topology I setup the first Switch to be on VLAN 1 This can be done on the configuration terminal: int valn 1 After that when we enter the interface we assign it to the address 10.10.10.1 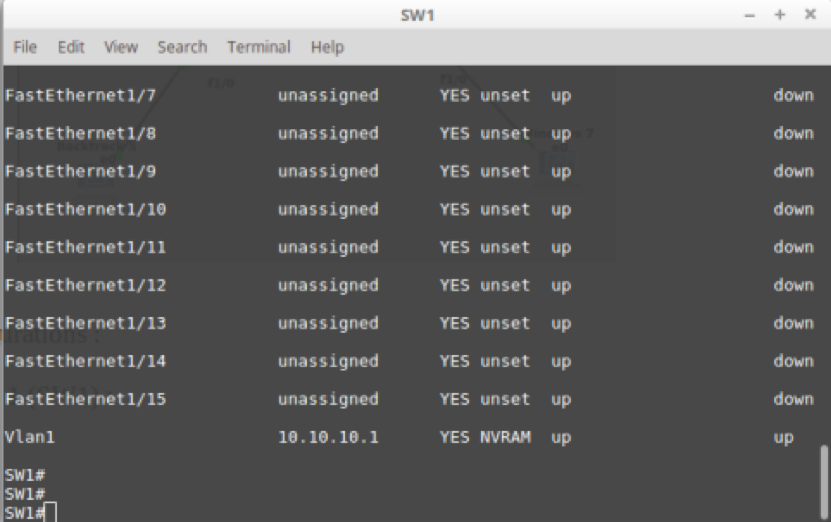
In this case, the attacker is on port fa1/0 , the trunk port is on port fa1/1. 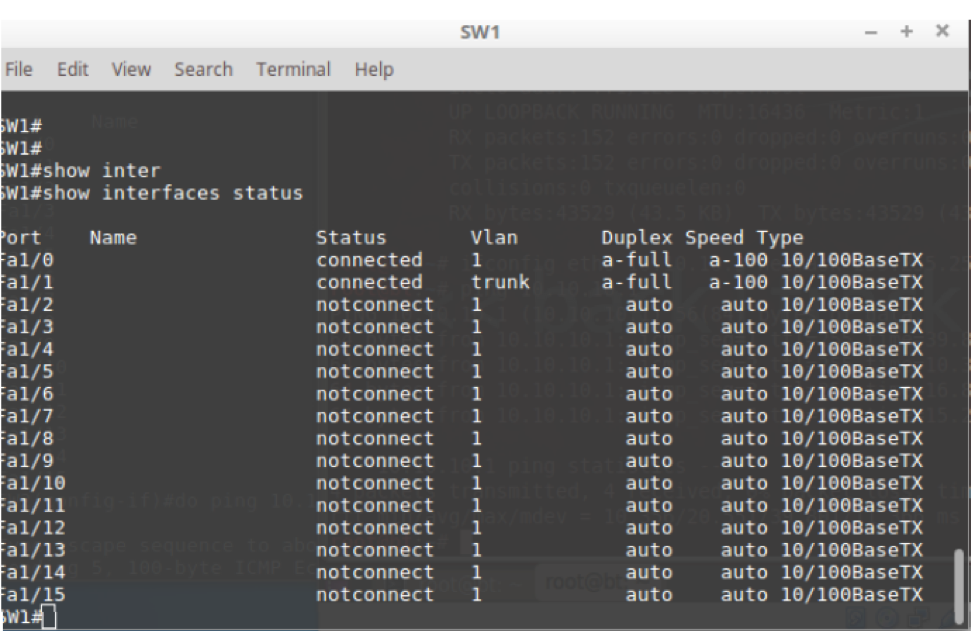
Moreover, on switch 2, we gave VLAN 2 an IP address of 10.10.11.1 and VLAN 1 an IP address on the same network as Switch 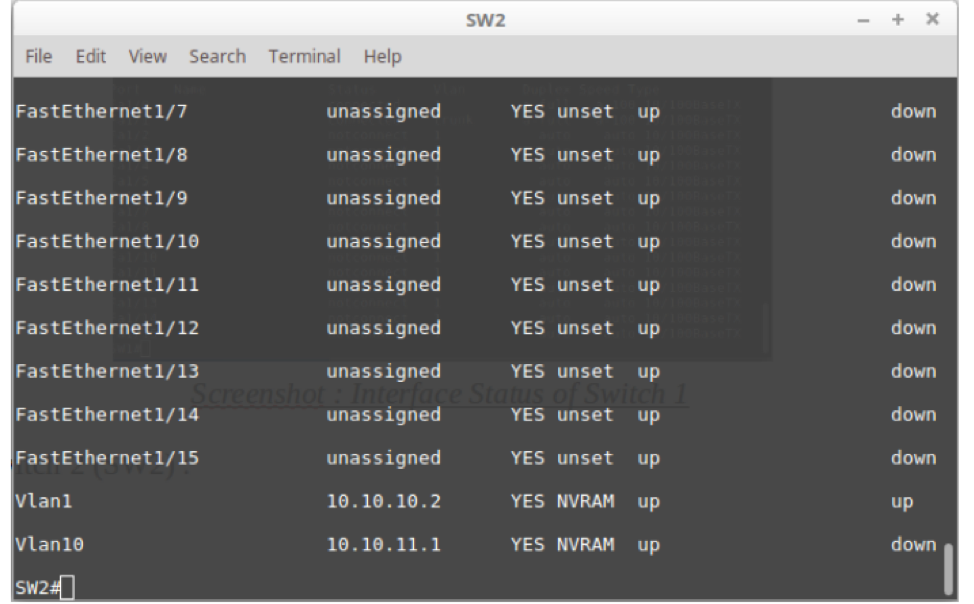
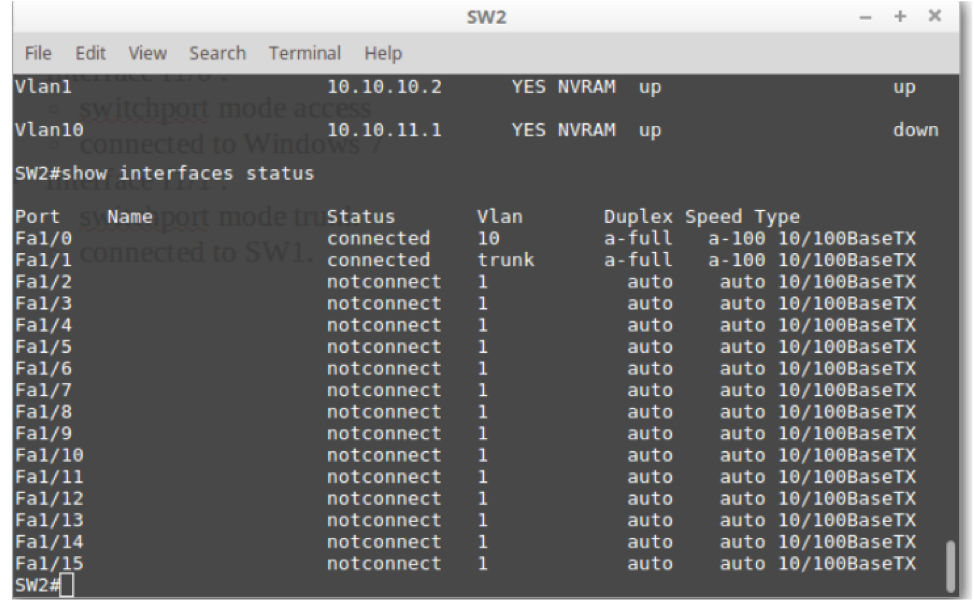
Now, if we take a look at port fa1/0 it will have the victim connected to it, and when we look at the other port, fa1/1, it will have the trunk port on it. The attacker now has an address of 10.10.10.3 on the first network. 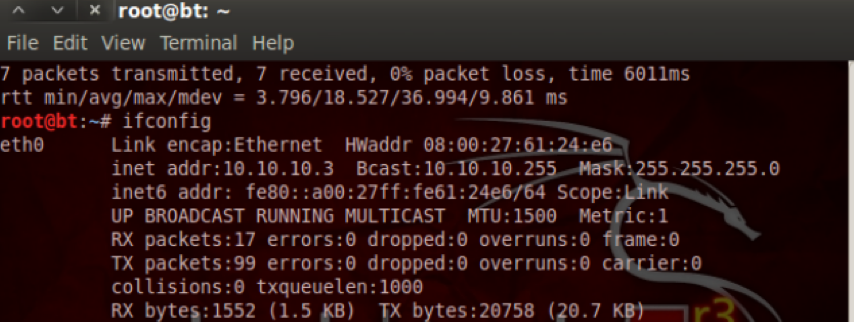
On the other hand the victim is on VLAN 10 and has an ip address of 10.10.10.1 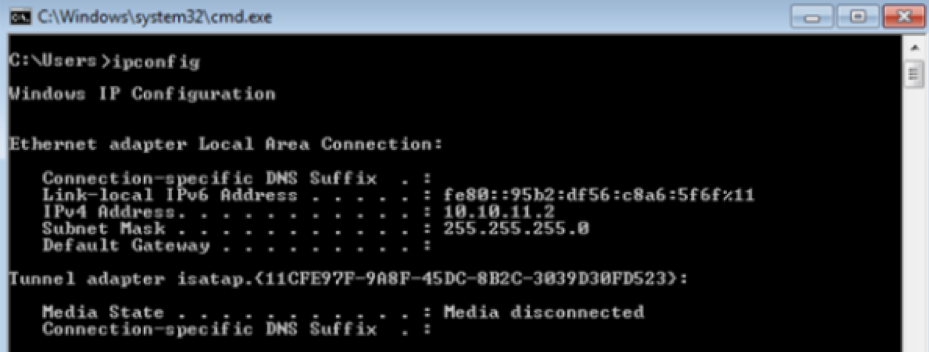
Now, we go to the terminal and run the Yersinia tool. 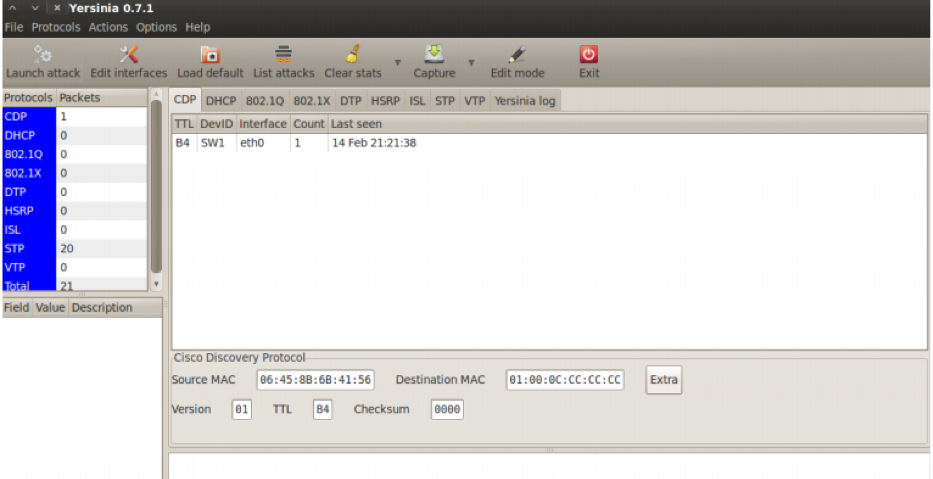
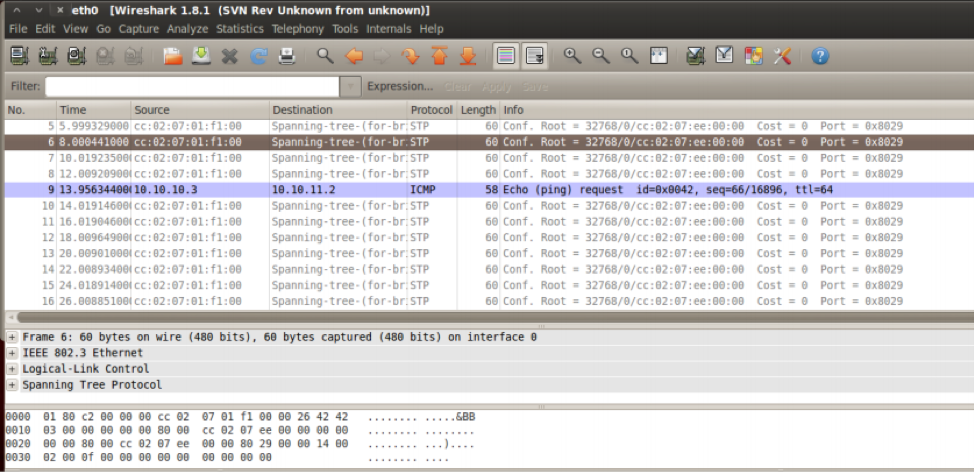
In order to perform the double tagging attack we click on the 802.1Q header to perform the attack. 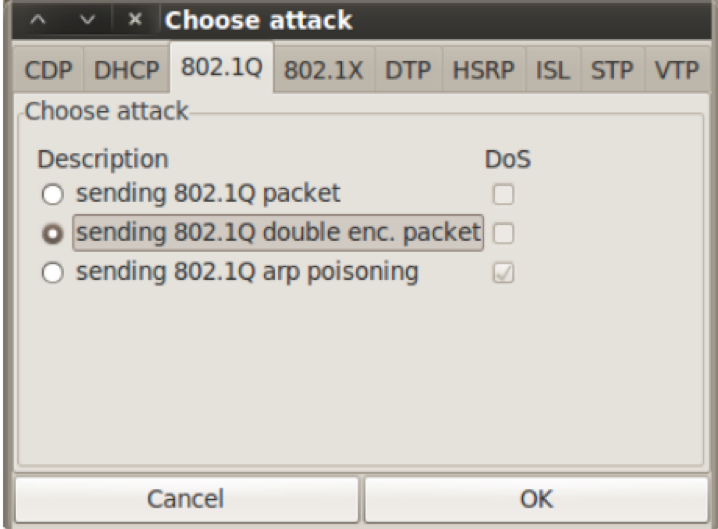 When we perform the attack we can see the capture on the attackers machine of an ICMP packet going through the VLAN and reaching the other network.
When we perform the attack we can see the capture on the attackers machine of an ICMP packet going through the VLAN and reaching the other network.
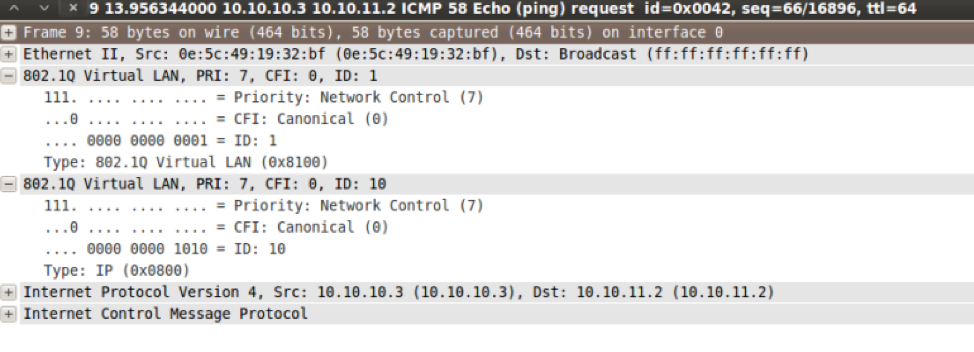
Looking closely at the packet we can see the VLAN double tags, the first one on VLAN 1 and the other on VLAN 10, it is worth noting that this is only shown from the attackers box.
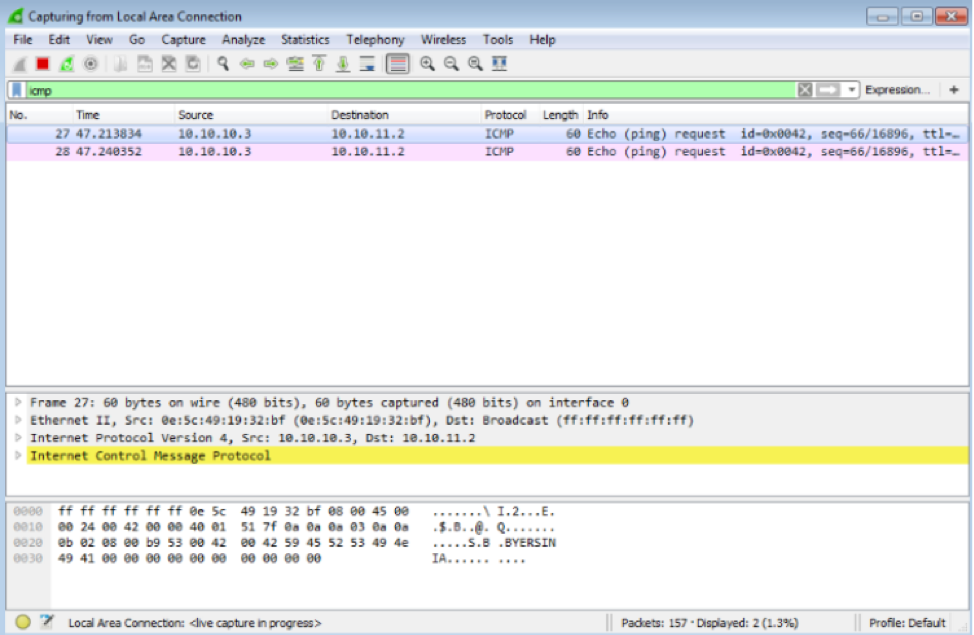
If we take a close look at the ICMP packet on the victims machine, we will see the ICMP request being received and no sign of any 802Q.1 header.
Mitigation the Attack
There are several common best practices that network and system administration use to defend against this attack, including:
- Disabling dynamic port on non-usable ports on the switch
- Ensuring that swithcports are set to no negotiate which by default disables DTP.
- Not using VLAN 1 for inbound management traffic, and picking any other VLAN dedicated to that purpose. In other words, prune VLAN 1 from all the trunks and from all the access ports that don’t require it
Conclusoin
This kind of attack becomes a risk due it’s capabilities to hopping VLANs, since the attacker can deliver frames to different VLAN without even using inter- VLAN routing. Nowadays, Cisco realized this vulnerability and they prevented it in newer versions such “Cisco IOS 12.2” which it configured to prevent double VLAN tagging.