Introduction
ARP is one of the most important networking protocol that other protocols rely on as it maps a mac address to an associated IP address. The attack we will be talking about is called ARP spoofing and is a type of Man-in-the-middle-attack in which the attacker tries to respond to ARP request with a forged packet.
Topology
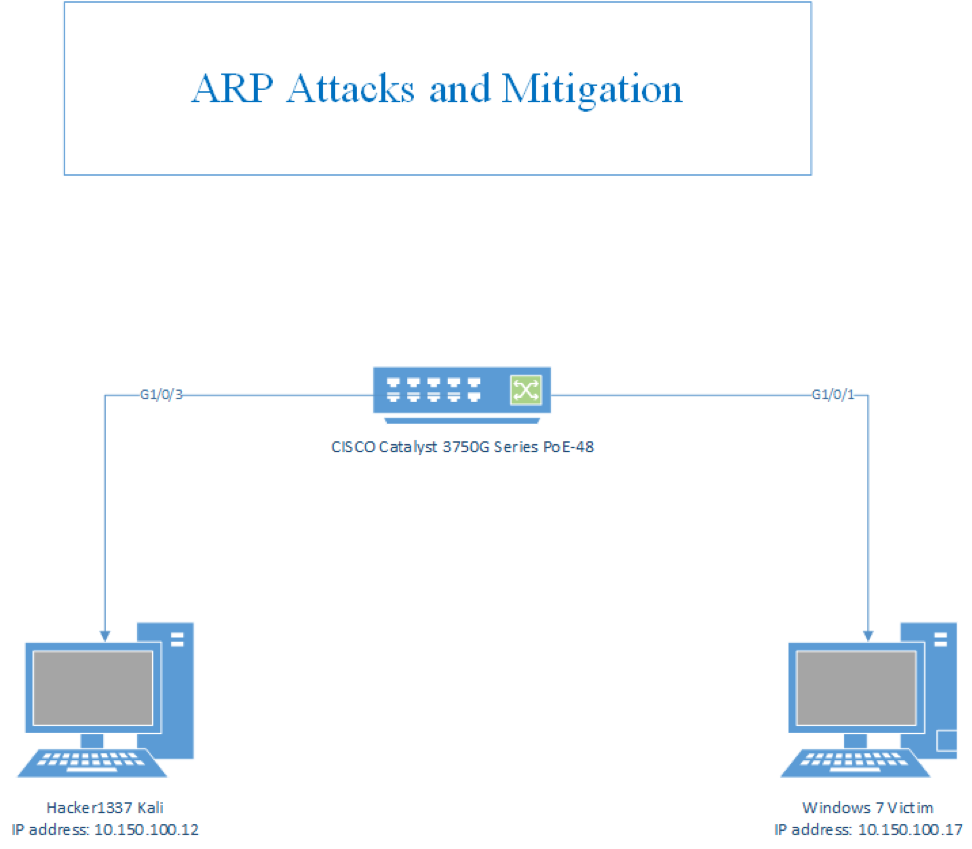
ARP Attacks:
ARP Spoofing
Using the arpspoof tool, which is available in Kali Linux, I spoofed one of the clients MAC address.
arpspoof command on Kali 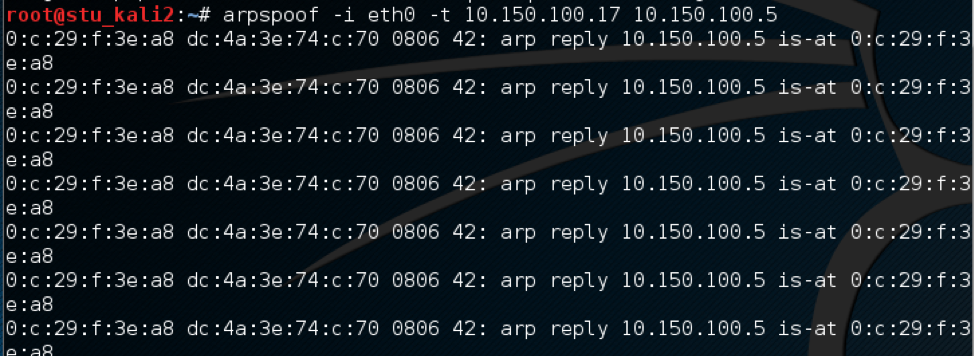 This will enable the attacker to inspect all traffic destined for
This will enable the attacker to inspect all traffic destined for 10.150.100.5 by redirecting to the Kali IP address then forward it back to the victim. As we can see in Wireshark capture. 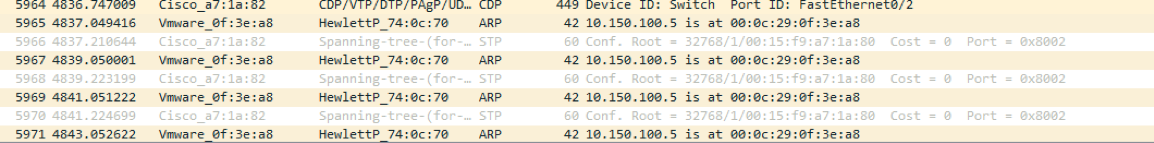
Dynamic ARP Inspection Mitigation
When we want to avoid invalid and malicious ARP packets, we can use Dynamic ARP Inspection (DAI). This feature work similarly to DHCP snooping, in that if a client sends a message that is recognized as malicious it will drop these illegitimate packets. We start the switch configuration by applying DAI on the switch in 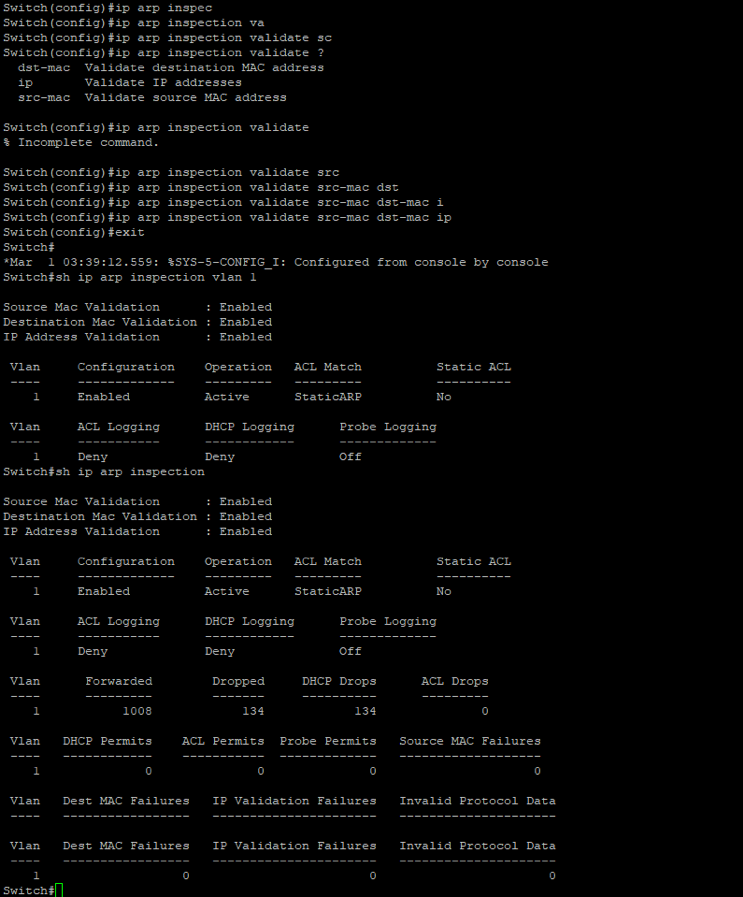 It’s worth notating that I applying the ACL “static ARP” which contains the IP and mac addresses for my clients. Additionally, if I rerun the attack again we won’t see the packets on the victim’s machine as the packets gets dropped when it reaches the switch and does not get forwarded. Additionally, the switch raises a lot of warnings to notify the network administrator as shown below.
It’s worth notating that I applying the ACL “static ARP” which contains the IP and mac addresses for my clients. Additionally, if I rerun the attack again we won’t see the packets on the victim’s machine as the packets gets dropped when it reaches the switch and does not get forwarded. Additionally, the switch raises a lot of warnings to notify the network administrator as shown below. 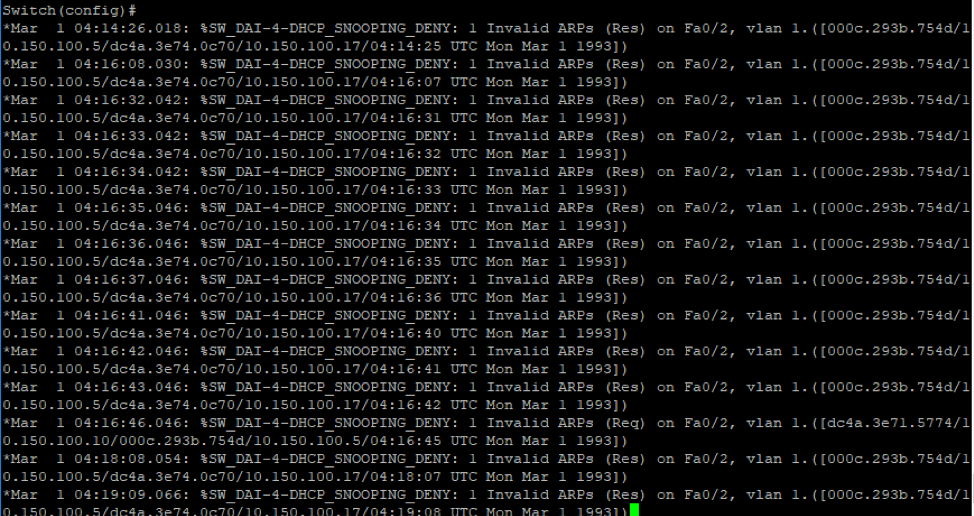
Introduction
IP Source Guard (IPSG) is a defense mechanism that is designed to prevent IP spoofing attacks. For instance, when someone wants to spoof the address of another host, this feature will prevent this spoofing because this IP address is not assigned by DHCP. IPSG works by relying on DHCP snooping and IP source bindings to match the IP address on untrusted Layer 2 networks.
Topology
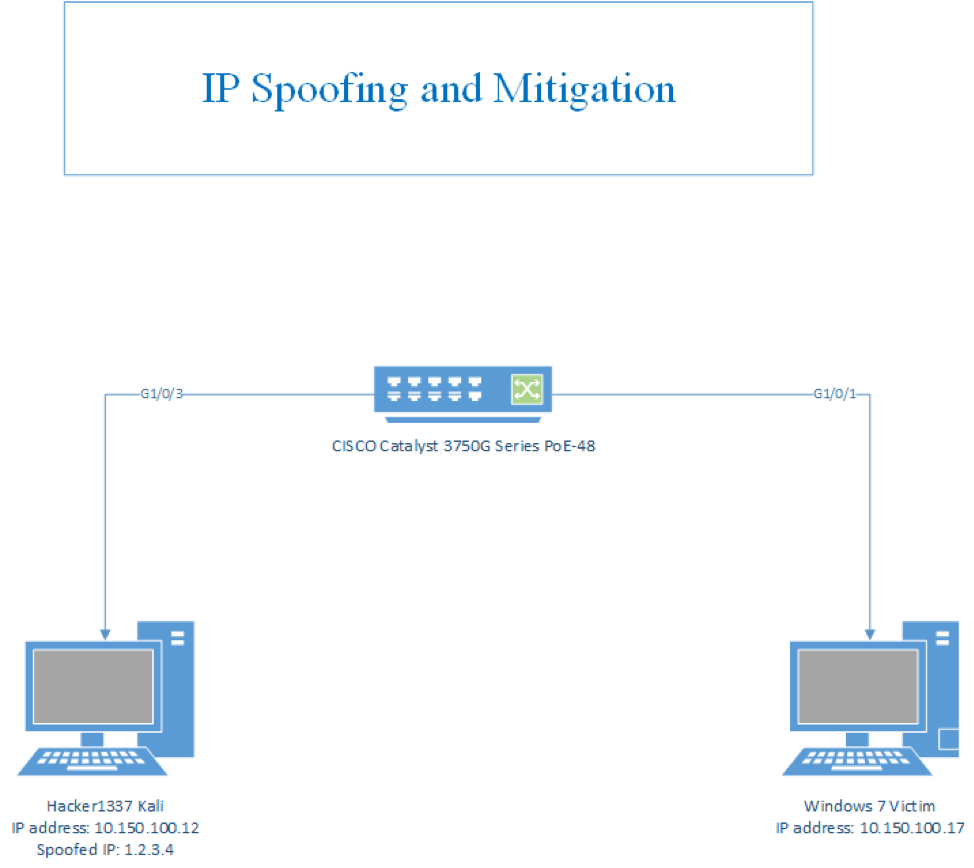
IP Attacks:
IP Spoofing
IP spoofing is an attack performed to achieve one of two goals: a DOS (Denial of Services) or unauthorized access to a network. We perform this attack by using Scapy. As shown below we build an IP header with a spoofed IP address and the destination of our target IP address.
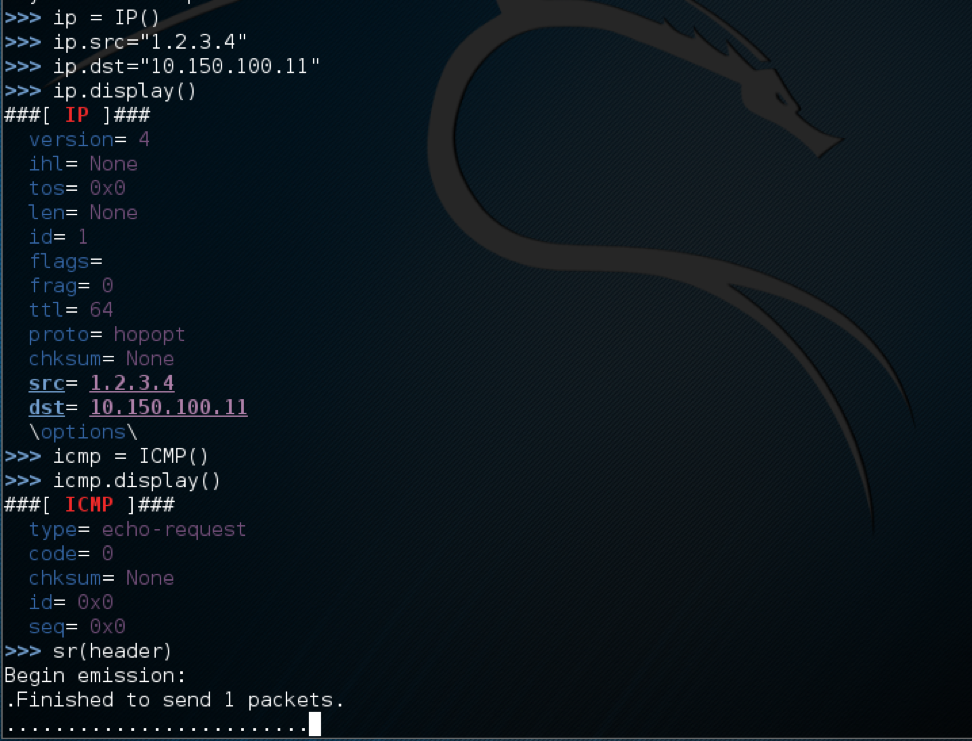
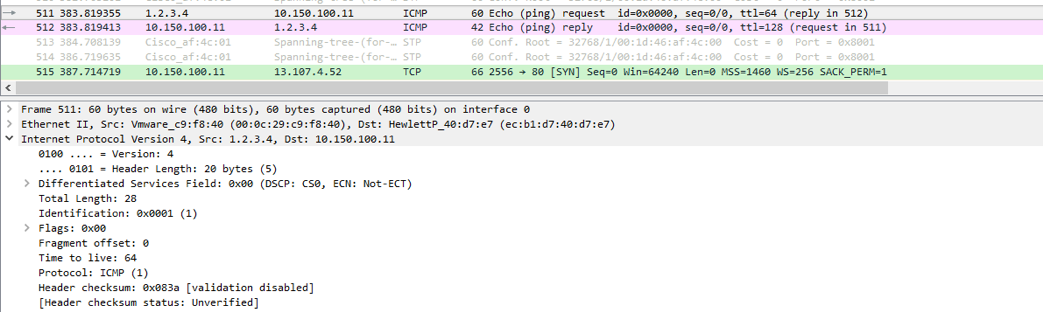
Also, it worth noting that in my topology the actual IP address of our Kali is 10.150.100.12, the reason this is working is there is no validation that maps the IP address to the mac address of the host that is sending the spoofed IP as we will see, this is how the mitigation works. Now if we look at Wireshark capture below, we see that the ICMP packet was sent to the target and the replay came back to the spoofed IP address.
IP Source Guard Mitigation
This mitigation relies on the DHCP database so we need to make sure we enable that as we discussed in previous mitigations. After this we include the IP source guard configuration to the switch as show below 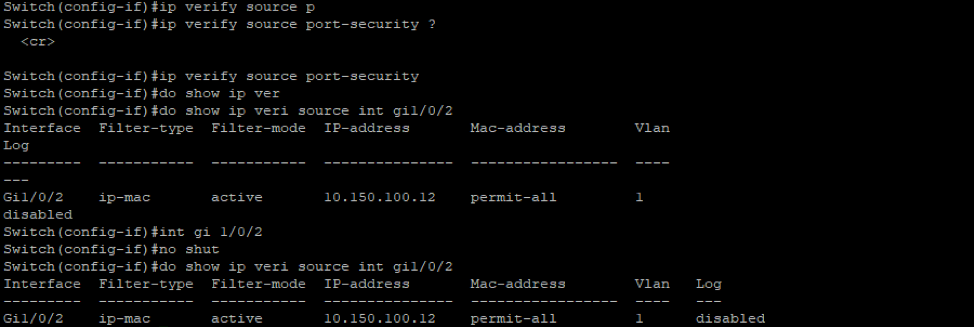
Now if we try to spoof an IP from scapy on Kali, the victim should not successfully respond back to that packet. If we take a look at the DHCP snooping database it show that the Kali mac address is associated with that IP address, and if tried to send a packet with different IP address other than that IP it should just get dropped.
Conclusoin
Spoofing an IP address was an issue since the attacker can spoof his IP address to do whatever he is not allowed to do like going into a specific network with someone’s else IP address, he was able to discover a specific network and exploit everything inside it and no one in the network can notices that. After “IP Source Guard”, it becomes much harder or we can say it’s impossible for the attacker to spoof his IP address. On the other hand, ARP spoofing is a real issue since it’s masquerading attempt to be someone else over the network and get everything that it’s belonging to him. However, Cisco came up with DAI on their switch as a solution for this issue, as we saw when the switch was configured with DAI the attack is being prevented and the switch drops illegitimated ARP packets. Hence, it’s preventing Man in the Middle Attack even if it takes one more step on configure static ARP list.